1. 引言
主要涉及知识点
- 二叉树的概念。
- 二叉查找树的概念跟常用操作。
- 二叉树的遍历(先序遍历、中序遍历、后序遍历、层序遍历)。
其他
- 队列(层序遍历用到)。
最后留了两个思考的点
- delete 为什么要 return t。
- 为什么是 t->right = delete(x, t->right) 而不直接 delete(x, t->right)。
2. 概念
树是一种非线性数据格式,计算机里面非常有用的数据格式之一,最常用的其中就有二叉树、二叉查找树,
二叉树:每个节点都不能有多余两个儿子的一棵树 二叉查找树:对于树种的每一个节点 X ,都满足它的左子树的关键字小于 X 的关键字,右子树的关键字大于 X 的关键字并且 X 的关键字是不重复的。
二叉查找树是基础性数据结构,用于构建更为抽象的数据结构,如集合、multiset、关联数组等,二叉树的优点是插入、查找时间复杂度低 O(logN)。
3. 二叉查找树的思路
定义一颗二叉查找树的结构体
typedef struct tree_node
{
element_type element; //节点关键字
struct tree_node *left; //左子树
struct tree_node *right; //右子树
} *search_tree;
typedef search_tree position;
一棵标准二叉查找树需要实现的方法
search_tree make_empty(search_tree t);
position find(element_type x, search_tree t);
position find_min(search_tree t);
position find_max(search_tree t);
search_tree insert(element_type x, search_tree t);
search_tree delete(element_type x, search_tree t);
element_type retrieve(position p); //检索值
麻烦一点儿的在删除。 删除的节点有三种情况:
- 是树叶——直接 delete。
- 有一个儿子:父节点直接指向子节点。
- 有两个儿子:右子树最小的数据代替该节点,并删除那个节点(右子树最小节点、直接递归删)。
4. 二叉树遍历
- 先序遍历:root 节点->左节点->右节点。
- 中序遍历:左节点->root 节点->右节点。
- 后序遍历:左节点->右节点->root 节点。
- 层序遍历:逐层遍历。 重点说层序遍历。
5. 具体实现
queue.h头文件,就是一个队列,具体实现代码参照队列那篇文章
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "bitree.h"
#define error(str) fatal_error(str)
#define fatal_error(str) fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", str),exit(1)
struct node;
typedef search_tree queue_element_type;
typedef struct node *ptr_to_node;
typedef ptr_to_node queue;
queue create_queue();
void queue_make_empty(queue q);
int is_empty(queue q);
void enqueue(queue_element_type x, queue q);
void dequeue(queue q);
queue_element_type front(queue q);
queue_element_type front_and_dequeue(queue q);
void dispose_queue(queue *q);
bitree.c 文件
/**
* 二叉查找树
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include "queue.h"
#include "bitree.h"
struct tree_node
{
element_type element; //节点关键字
struct tree_node *left; //左子树
struct tree_node *right; //右子树
};
search_tree make_empty(search_tree t)
{
if (NULL != t) {
make_empty(t->left);
make_empty(t->right);
free(t);
}
return NULL;
}
position find(element_type x, search_tree t)
{
if (NULL == t)
return NULL;
if (t->element > x)
return find(x, t->left);
else if(t->element < x)
return find(x, t->right);
else
return t;
}
position find_min(search_tree t)
{
/*非递归*/
/*if (NULL != t)
while (t->left != NULL)
t = t->left;
return t;*/
//递归
if (NULL == t)
return NULL;
if (NULL == t->left)
return t;
else
return find_min(t->left);
}
position find_max(search_tree t)
{
/*递归*/
/*if (NULL == t)
return NULL;
if (NULL == t->right)
return t;
else
return find_max(t->right);*/
/*非递归*/
if (NULL != t)
while (t->right != NULL)
t = t->right;
return t;
}
search_tree insert(element_type x, search_tree t)
{
if (NULL == t) {
t = (search_tree)malloc(sizeof(struct tree_node));
if (NULL == t)
fatal_error("out of space");
else {
t->element = x;
t->left = t->right = NULL;
}
} else if (x < t->element) {
t->left = insert(x, t->left);
}
else if (x > t->element) {
t->right = insert(x, t->right);
}
return t;
}
search_tree delete(element_type x, search_tree t)
{
position temp_cell;
if ( NULL == t)
error("empty tree");
else if(x < t->element)
t->left = delete(x, t->left);
// delete(x, t->left); /*思考:为什么不直接 delete*/
else if (x > t->element)
t->right = delete(x, t->right);
// delete(x, t->right); /*思考:为什么不直接 delete*/
else if (t->left && t->right) { // 有两个儿子 找右子树最小节点
temp_cell = find_min(t->right);
t->element = temp_cell->element; // 右子树最小关键字替换上来
// delete right child
delete(temp_cell->element, t->right);
} else { // 一个 or 0 个节点,不左还是右都是直接跨过 t 直接指向该节点
temp_cell = t;
if (t->left == NULL)
t = t->right;
else if (t->right == NULL)
t = t->left;
free(temp_cell);
temp_cell = NULL;
}
return t; //是何用意?
}
element_type retrieve(position p)
{
return p->element;
}
void print_tree(search_tree t, int type)
{
if (NULL == t) {
fatal_error("empty tree");
}
// 先序遍历
if (type == 1)
printf("%d ", t->element);
if (t->left)
print_tree(t->left, type);
// 中序遍历
if (type == 2)
printf("%d ", t->element);
if (t->right)
print_tree(t->right, type);
// 后序遍历
if (type == 3)
printf("%d ", t->element);
}
void print_layer(search_tree t)
{
queue q;
position p;
q = create_queue();
enqueue(t, q);
while (is_empty(q) != 1) {
p = front(q);
printf("%d ", p->element);
if (NULL != p->left)
enqueue(p->left, q);
if (NULL != p->right)
enqueue(p->right, q);
dequeue(q);
}
}
void test()
{
search_tree t;
int i, x;
t = make_empty(NULL);
srand( (unsigned)time(NULL) );
for( i = 0; i < 10; i++ )
t = insert(rand() % 50, t);
printf("\n先序遍历:");
print_tree(t, 1);
printf("\n中序遍历:");
print_tree(t, 2);
printf("\n后序遍历:");
print_tree(t, 3);
printf("\n层次遍历:");
print_layer(t);
printf("\n");
printf("max:%d\n", find_max(t)->element);
printf("min:%d\n", find_min(t)->element);
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
test();
return 0;
}
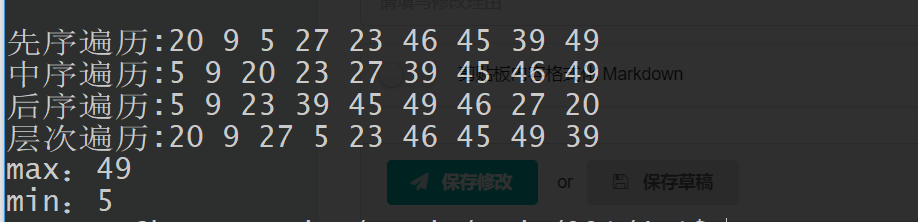
7. 运行截图