1. 前言
前一节用分离链接法解决了冲突问题,同时该算法也具有自己的缺点。
- 需要指针,新单元分配地址需要时间,导致速度减慢。
- 需要实现另一种数据结构(单链表)。
所以就有了开放地址法,如其名 开放地址 就是把其他地址也开放出来 比如在 分离链接法里面 hash 值为 0 的单元只映射 hash(x) = 0 的关键字,而在开放地址法里面就会把这些地址开放给其他的关键字,开放地址法:当有冲突时,就尝试选择另外的单元,直到找出空单元为止 那么他们又通过什么规则来确定映射关系以及寻找另外的单元的呢?这就是下面要说的 线性探测 跟 平方探测。
2. 线性探测 & 平方探测
线性探测 顾名思义,就是一个接一个的寻找,比如 hash(x) = 0;在 0 单元上发生冲突,就往下探测 1、2、3 …直到找到一个空单元为止。
平方探测 跟名字一样,就是当冲突发生时用二次函数来作为寻找单元的计算方法,如 hash(x) = 0;在 0 单元上发生冲突,下一个位置为:F(i) = i^2 来探测,i 第几次探测。
3. 实现
散列表的结构图如下:
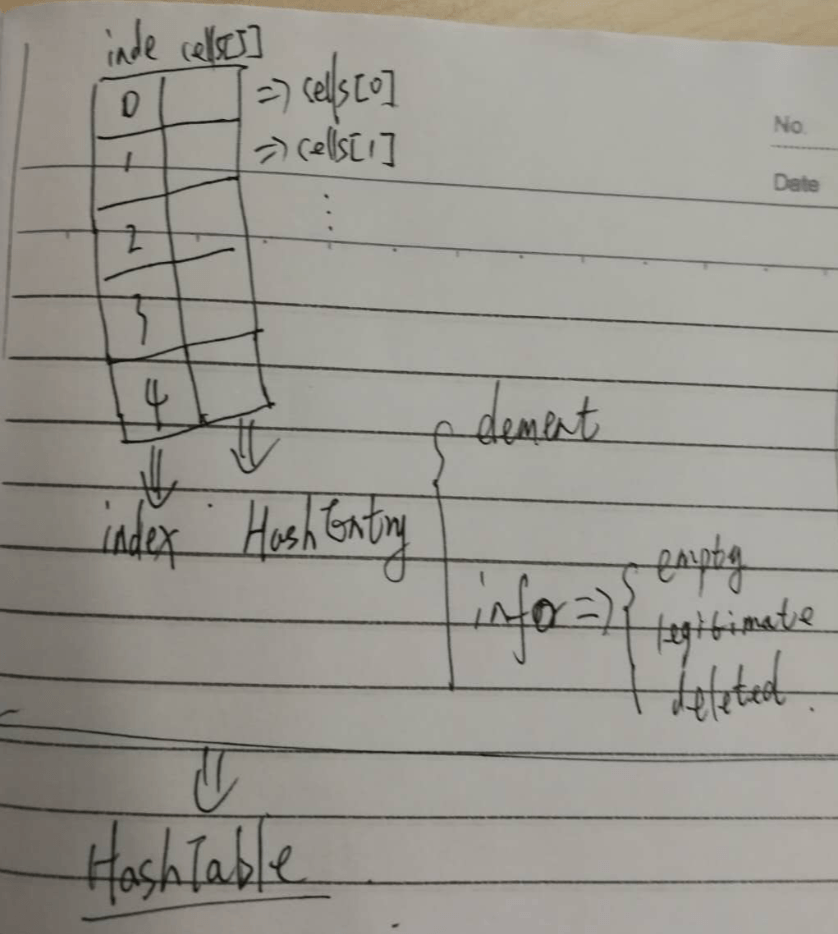
hash_quad.h 头文件定义
typedef unsigned int index;
typedef char* element_type;
typedef index position;
struct hash_table_node;
typedef struct hash_table_node *hash_table;
index hash(element_type key, int table_size);
hash_table initialize_table(int table_size);
void destroy_table(hash_table h);
position find(element_type key, hash_table h);
void insert(element_type key, hash_table h);
element_type retrieve(position p, hash_table h);
void delete(element_type key, hash_table h);
int next_prime(int table_size);
void random_hash_table(hash_table h, int len);
void print_hash_table(hash_table h);
void test();
enum kind_of_entry { legitimate, empty, deleted };
struct hash_entry
{
element_type element;
enum kind_of_entry info;
};
typedef struct hash_entry cell;
struct hash_table_node
{
int table_size;
int size;
cell *pcell_arr;
};
hash_quad 实现
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <math.h>
#include "hash_quad.h"
#define error(str) fatal_error(str)
#define fatal_error(str) fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", str), exit(1)
index hash(element_type key, int table_size)
{
unsigned int hash_value = 0;
while (*key != '\0') {
hash_value = (hash_value << 5) + *key++;
}
return hash_value % table_size;
}
int next_prime(int table_size)
{
int i, j = 2, k;
for (i = table_size; i > 0; i--) {
k = sqrt(i);
while (j <= k) {
if (i % j == 0)
break;
j++;
}
if (j > k)
break;
}
return i;
}
hash_table initialize_table(int table_size)
{
int min_table_size = 5;
hash_table h;
int i;
if ( table_size < min_table_size) {
error(" Table size is too small");
return NULL;
}
h = (hash_table)malloc(sizeof(struct hash_table_node));
if (NULL == h)
fatal_error("out of space");
h->table_size = next_prime(table_size);
h->size = 0;
h->pcell_arr = malloc(sizeof(struct hash_entry) * h->table_size);
if (NULL == h->pcell_arr)
fatal_error("out of space");
for (i = 0; i < h->table_size; i++) {
h->pcell_arr[i].info = empty;
}
return h;
}
position find(element_type key, hash_table h)
{
position current_pos;
int i;
i = 0;
current_pos = hash(key, h->table_size);
while (h->pcell_arr[current_pos].info != empty && h->pcell_arr[current_pos].element != key) {
// 线性探测
// current_pos += 1;
// 平方探测
current_pos += 2 * ++i - 1;
if (current_pos >= h->table_size)
current_pos -= h->table_size;
}
return current_pos;
}
void insert(element_type key, hash_table h)
{
position pos;
if (h->size > 0.8 * h->table_size) {
printf("超出 0.8 的装填因子,需要扩容\n");
return;
}
pos = find(key, h);
if (h->pcell_arr[pos].info != legitimate) {
h->pcell_arr[pos].info = legitimate;
h->pcell_arr[pos].element = key;
h->size++;
}
}
void destroy(hash_table h)
{
if (NULL == h)
error("Hash Table is NULL");
int i;
free(h->pcell_arr);
free(h);
}
void delete(element_type key, hash_table h)
{
position pos;
pos = find(key, h);
if (h->pcell_arr[pos].info == legitimate) {
h->pcell_arr[pos].info = deleted;
free(h->pcell_arr[pos].element);
h->size--;
}
}
void random_hash_table(hash_table h, int len)
{
char dictionary[52] = "adcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ";
int str_len, i, j;
srand((unsigned)time(NULL));
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
str_len = rand() % 8 + 1; // 1-8
char* str;
str = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * (str_len + 1));
for (j = 0; j < str_len; j++) {
str[j] = dictionary[rand() % 52];
}
str[j] = '\0';
insert(str, h);
str = NULL;
}
}
void print_hash_table(hash_table h)
{
index i;
for (i = 0; i < h->table_size; i++) {
printf("%d\t=>", i);
if (h->pcell_arr[i].info == legitimate)
printf("\t%s", h->pcell_arr[i].element);
printf("\n");
}
}
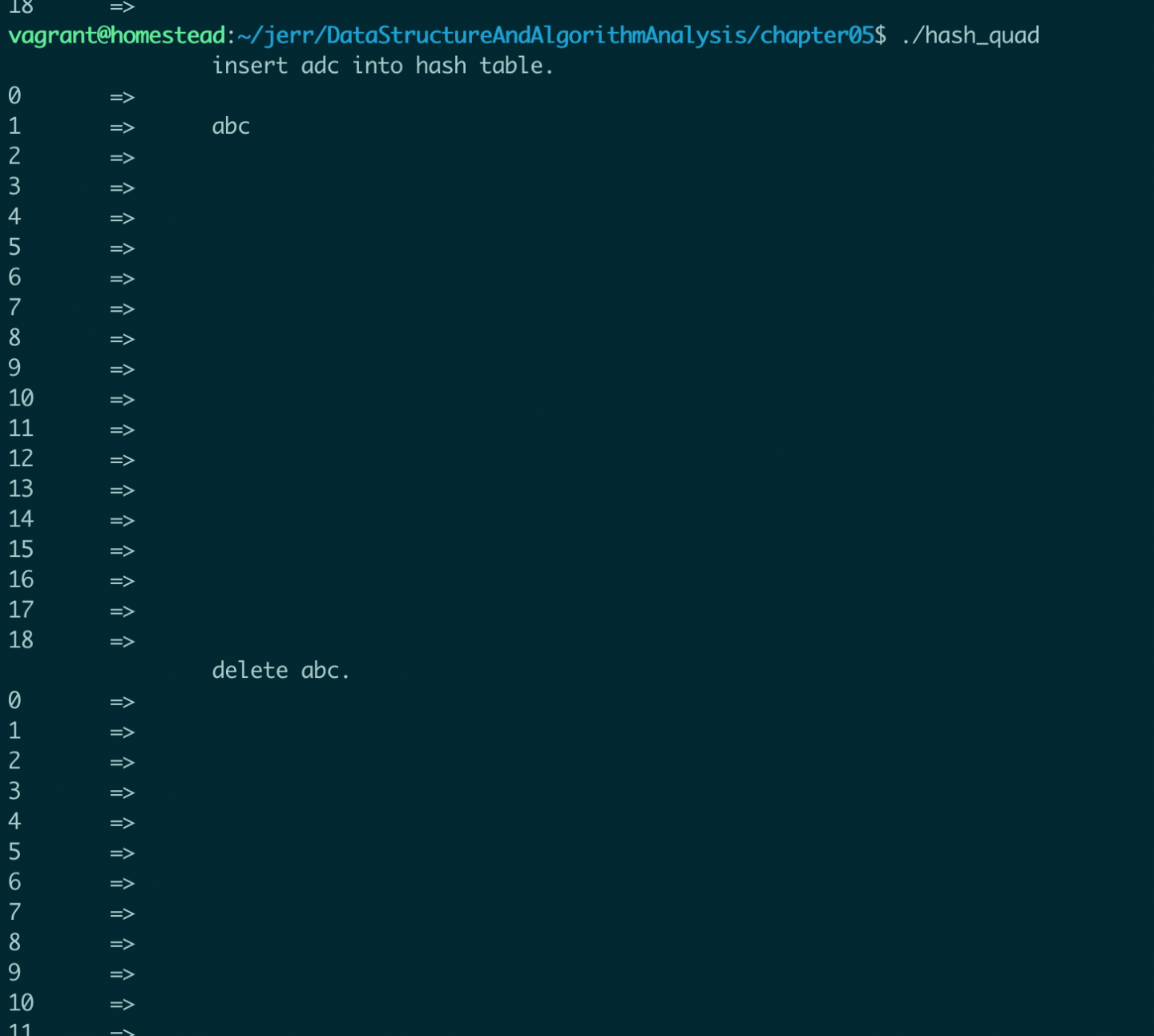
void test()
{
hash_table h;
h = initialize_table(22);
printf("\t\tinsert adc into hash table.\n");
char* str = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * 4);
str[0] = 'a';
str[1] = 'b';
str[2] = 'c';
str[3] = '\0';
insert(str, h);
print_hash_table(h);
printf("\t\tdelete abc.\n");
delete(str, h);
print_hash_table(h);
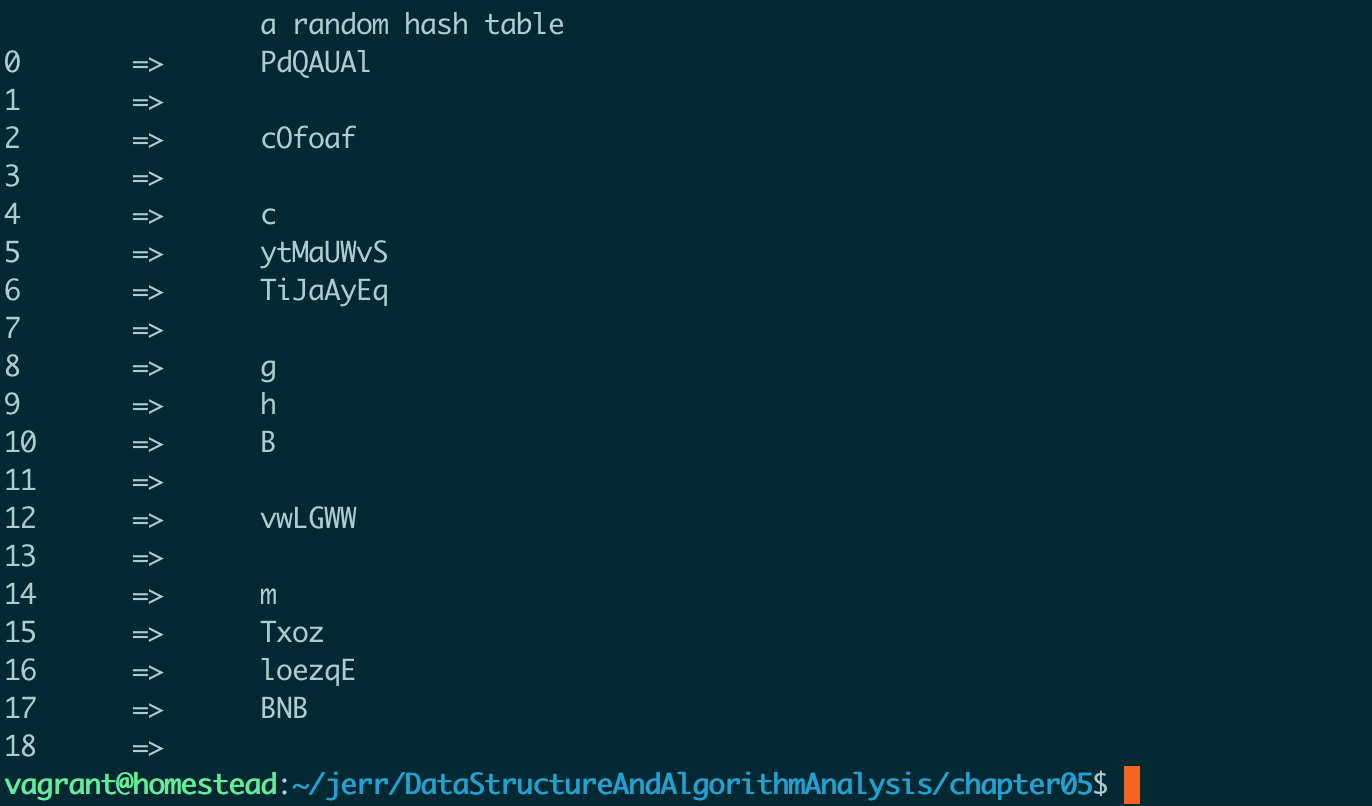
random_hash_table(h, 13);
printf("\t\ta random hash table\n");
print_hash_table(h);
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
test();
return 0;
}
4. 运行结果
5. 总结
- 开放地址法。
- 线性探测。
- 平方探测。
- 数组结构实现的散列表。
- c 的 char 类型 跟 字符串的理解。